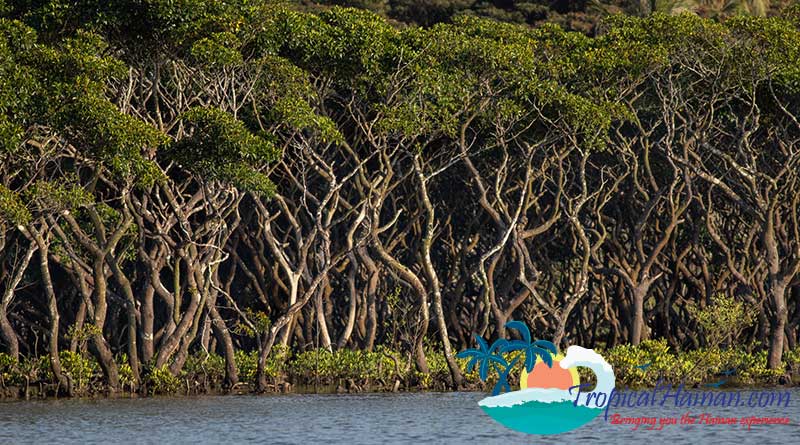
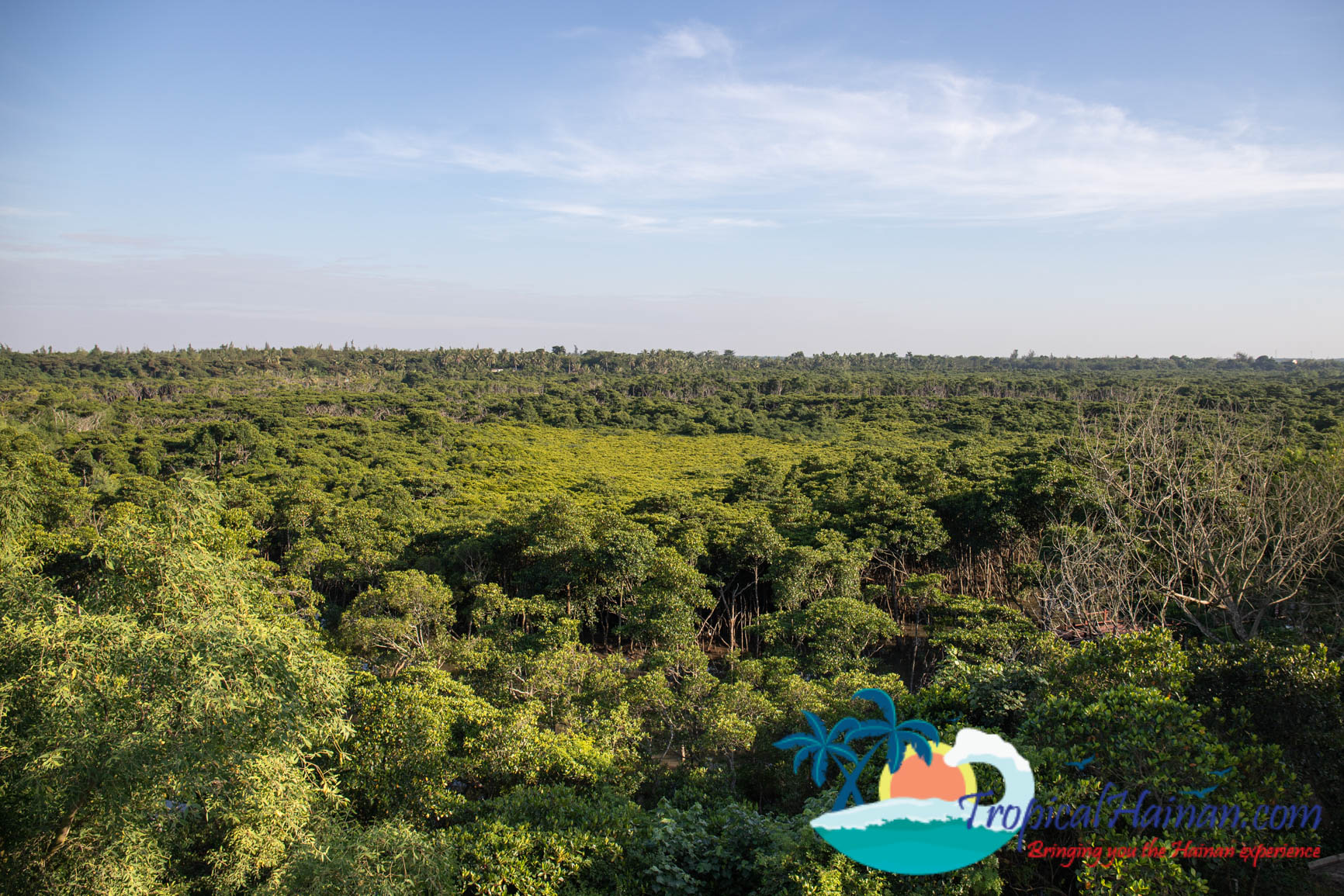
Dongzhaigang Mangroves, wetland ecosystems.
Hainan Dongzhaigang national nature reserve is located at the northern end of Hainan island, around 10km away from the Meilan international airport and 30 km away from downtown Haikou.

According to records from the Qiongzhou Prefecture, Dongzhaigang bay was formed in the 33rd year of the Wanli Emperor of the Ming Dynasty (1605) as a result of a massive earthquake (magnitude of around 7.5). The earthquake caused 72 villages to subside into the sea. The most prominent of these villages was Dongzhai village and the bay was given the name Dongzhaigang.
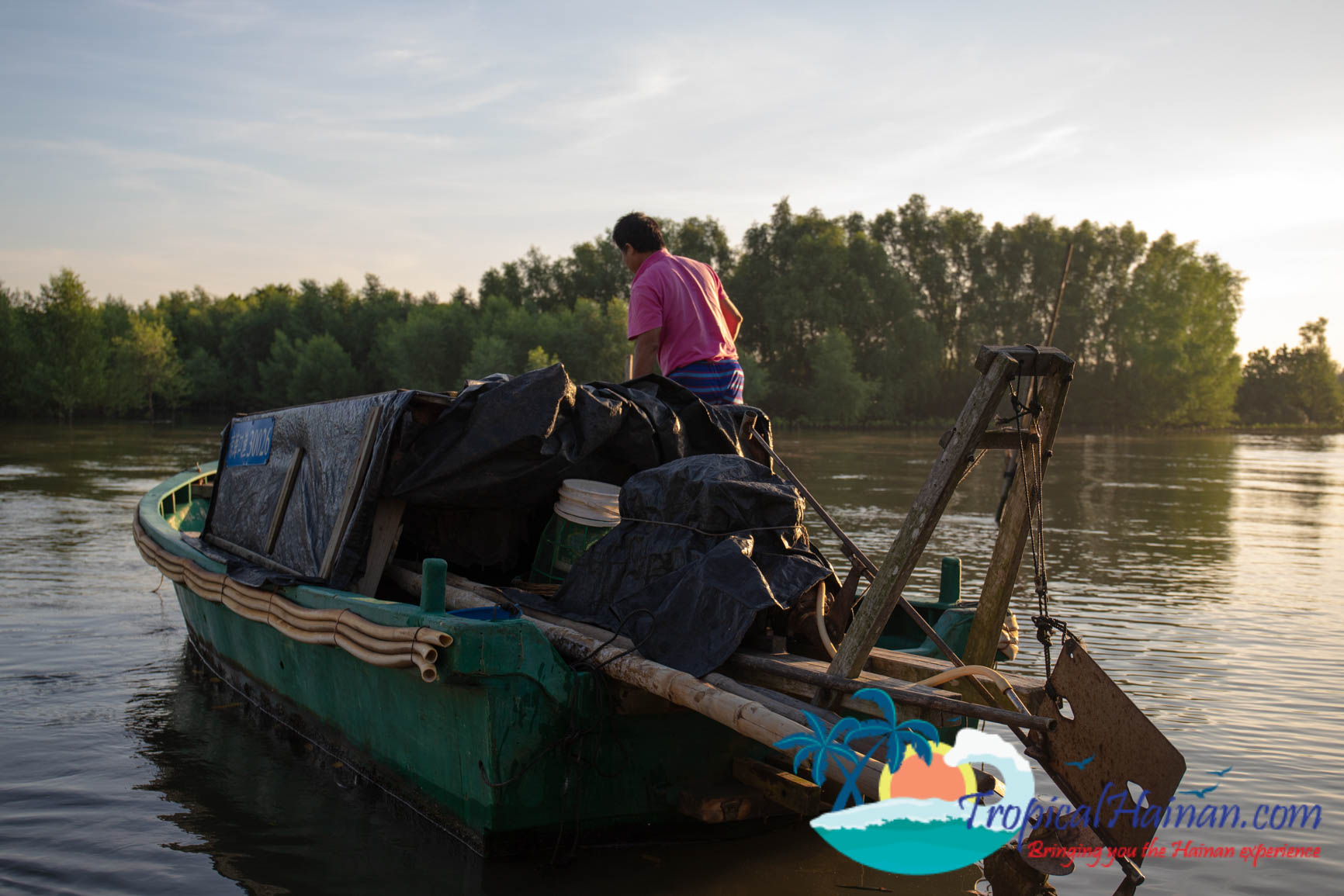

In January 1980, the Dongzhigang nature reserve was approved by the people’s government of Guangdong province. In July 1986, it was upgraded to a national nature reserve by the state council. It was the first national nature reserve to protect mangrove wetland ecosystems in China.
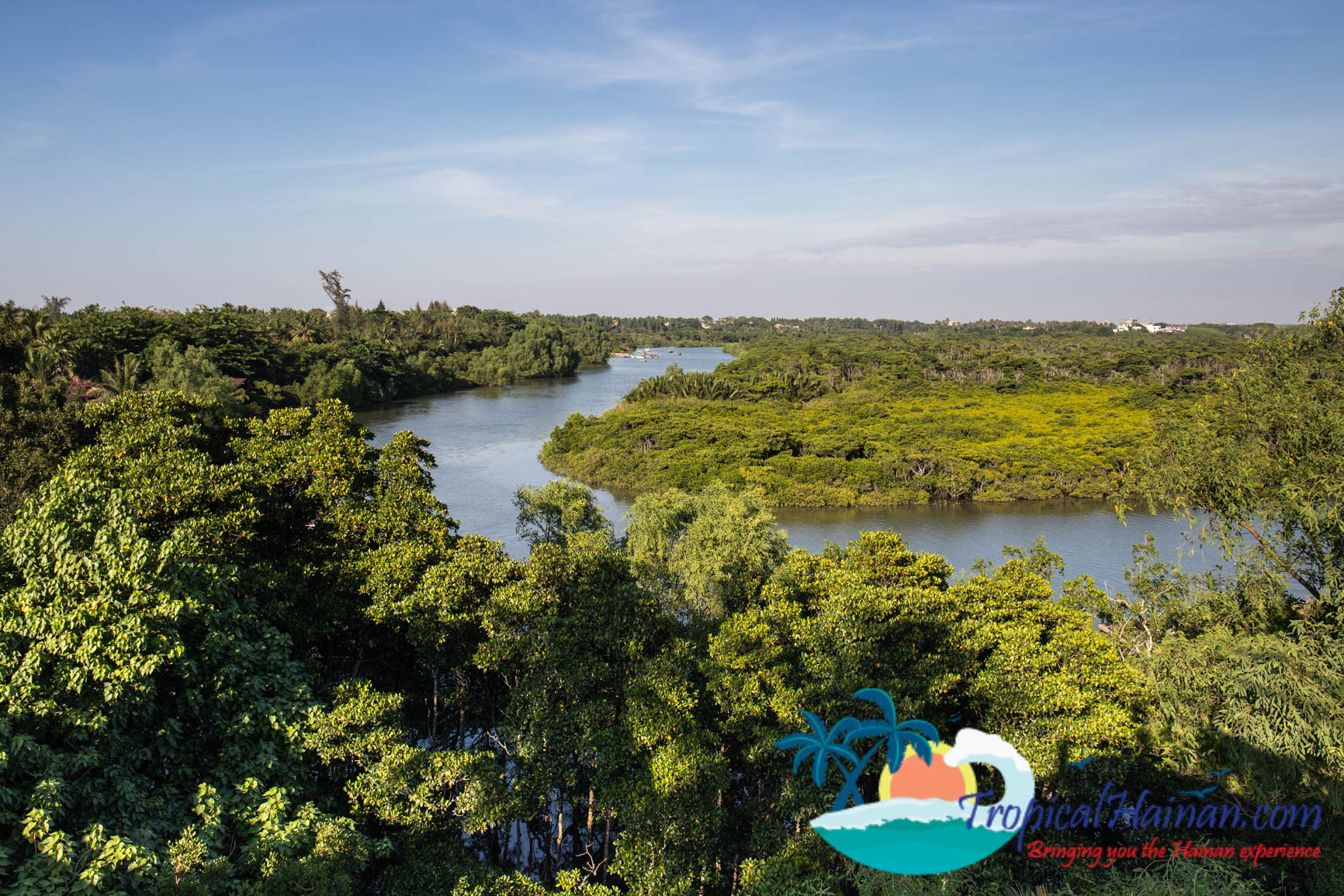

The reserve covers a total area of 3,337 hectares. The mangroves cover an area of 1771 hectares, and mudflats and waters account for the other 1566 hectares.
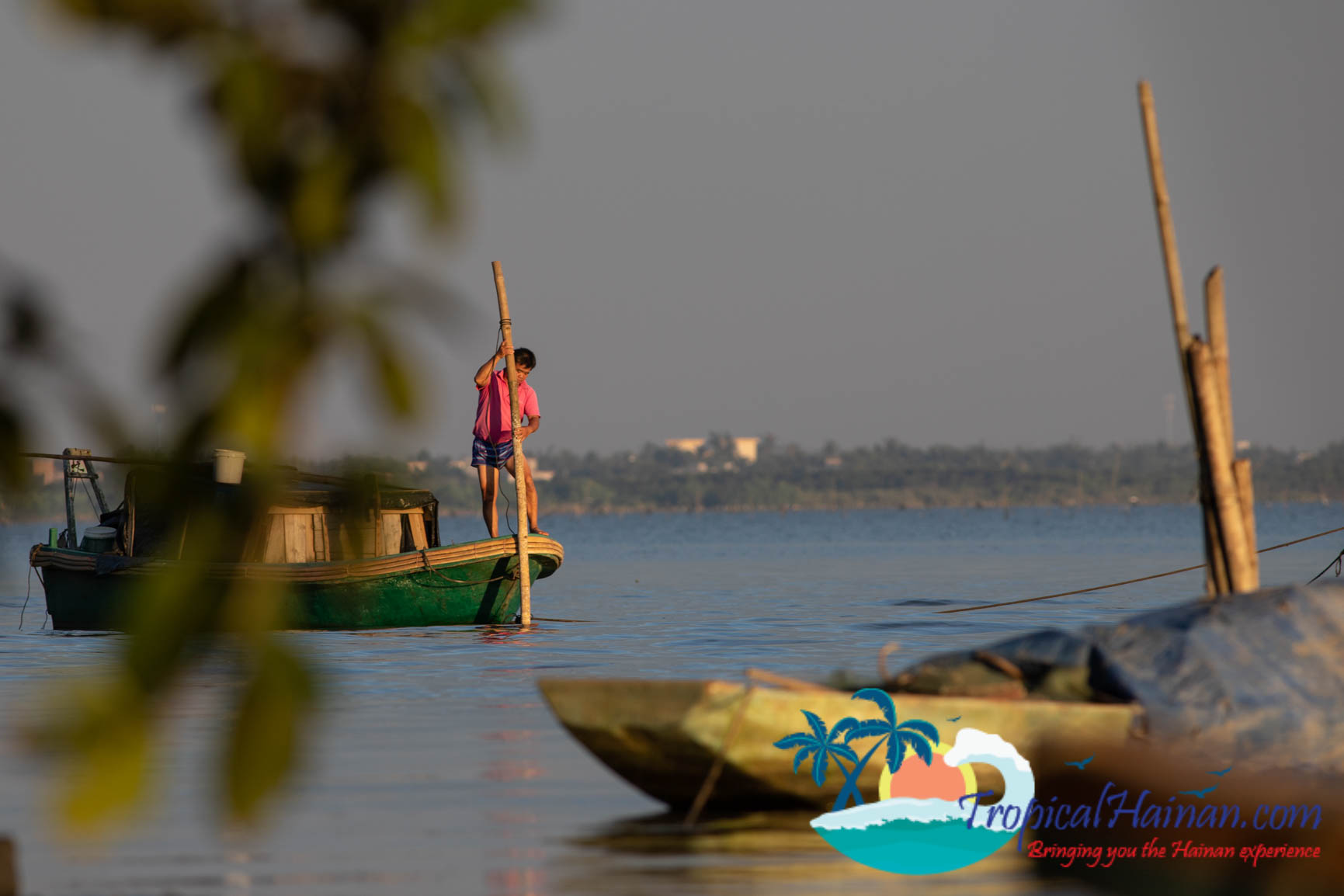

In China, mangroves are found in Hainan, Guangdong, Guangxi, Fujian, Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan. Their natural distribution runs from Sanya Bay, Hainan to Shacheng bay, Fujian. Fossil records show that China historically had as much as 250,000 hectares of mangroves. As late as the 1950’s, there were still around 50,000 hectares of mangroves.
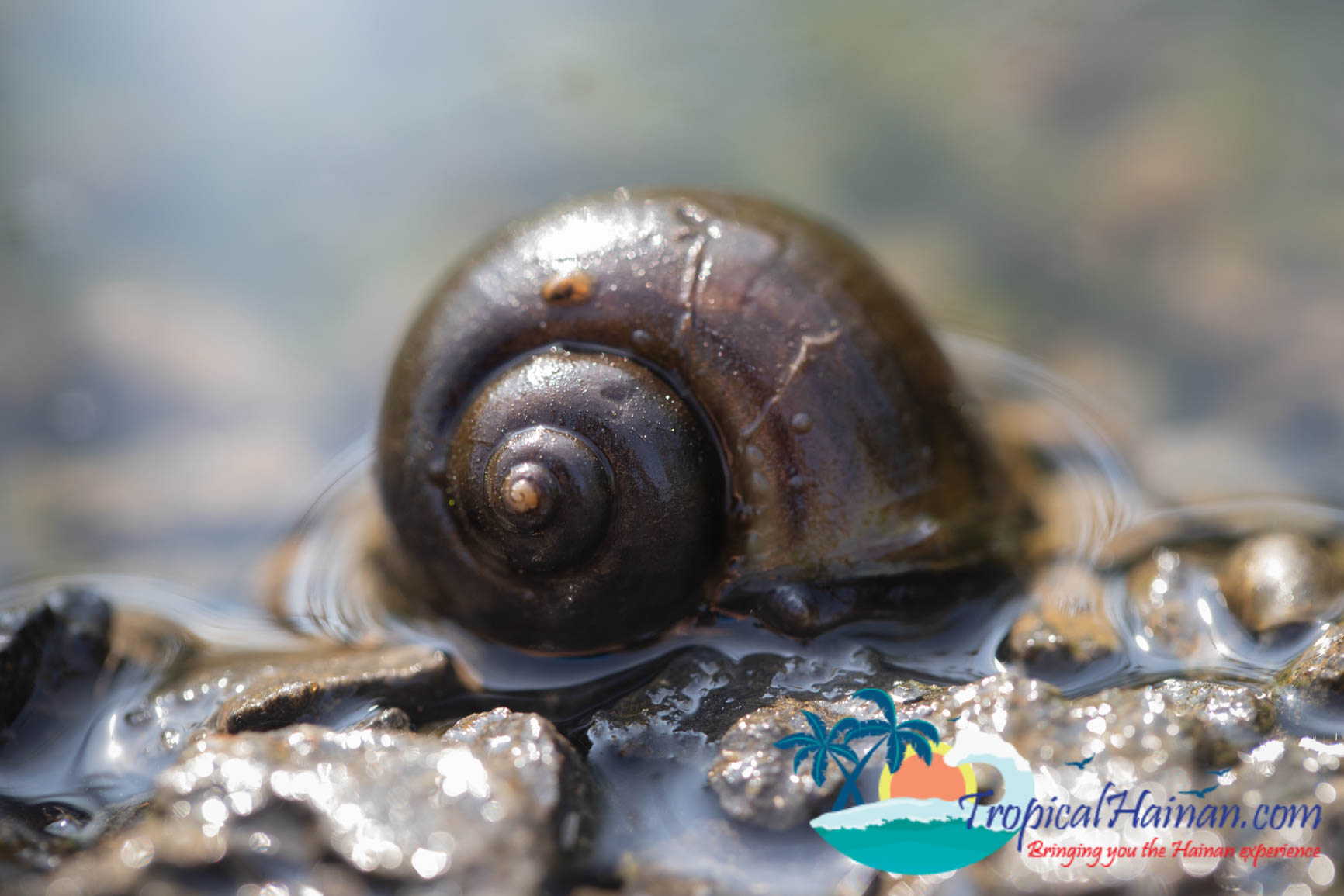

The mangroves are home to 19 families and 36 species of mangrove plants. There are 160 types of fish, 115 types of mollusk, 70 types of crustacean, and 208 types of birds.
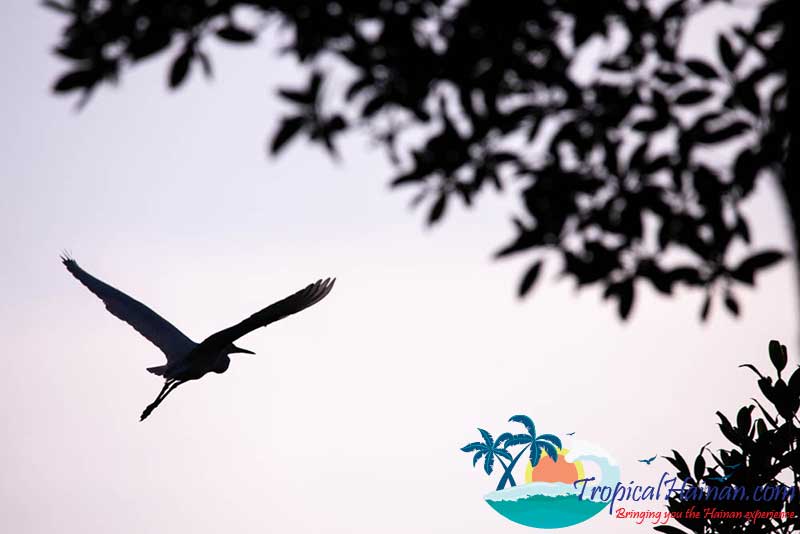
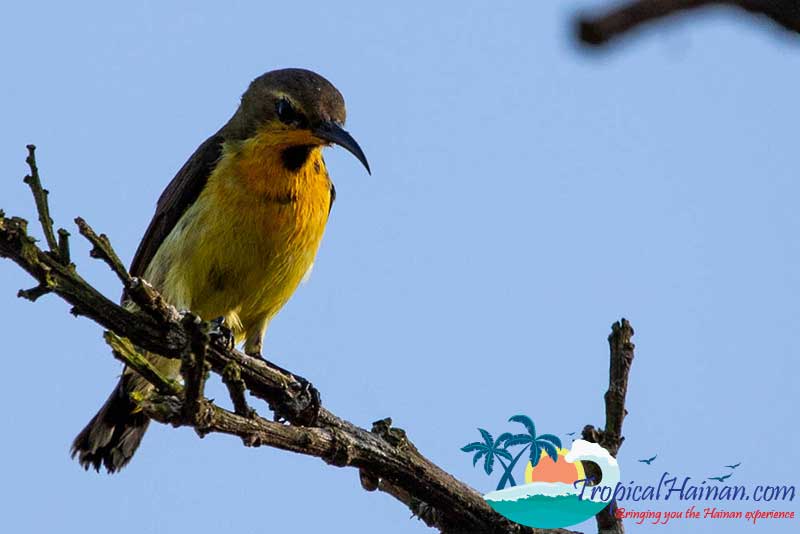


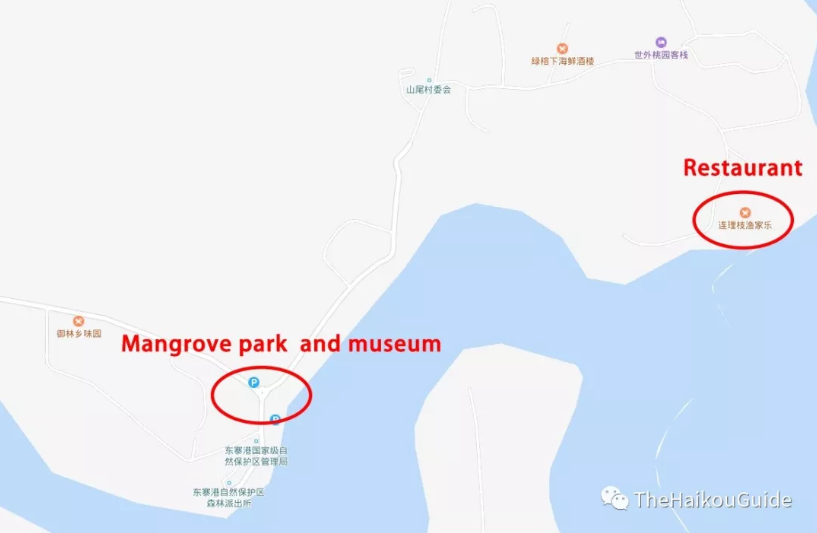
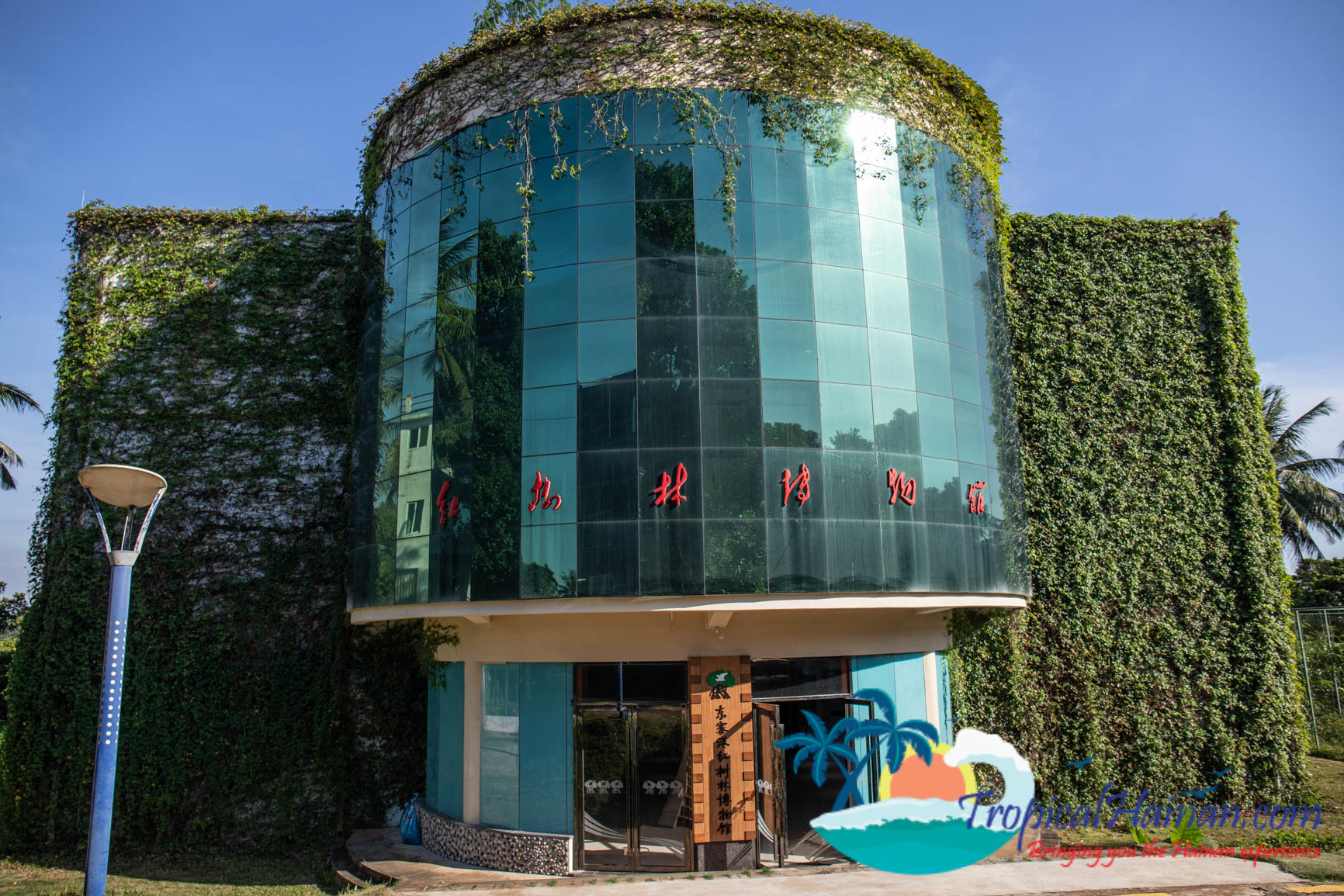
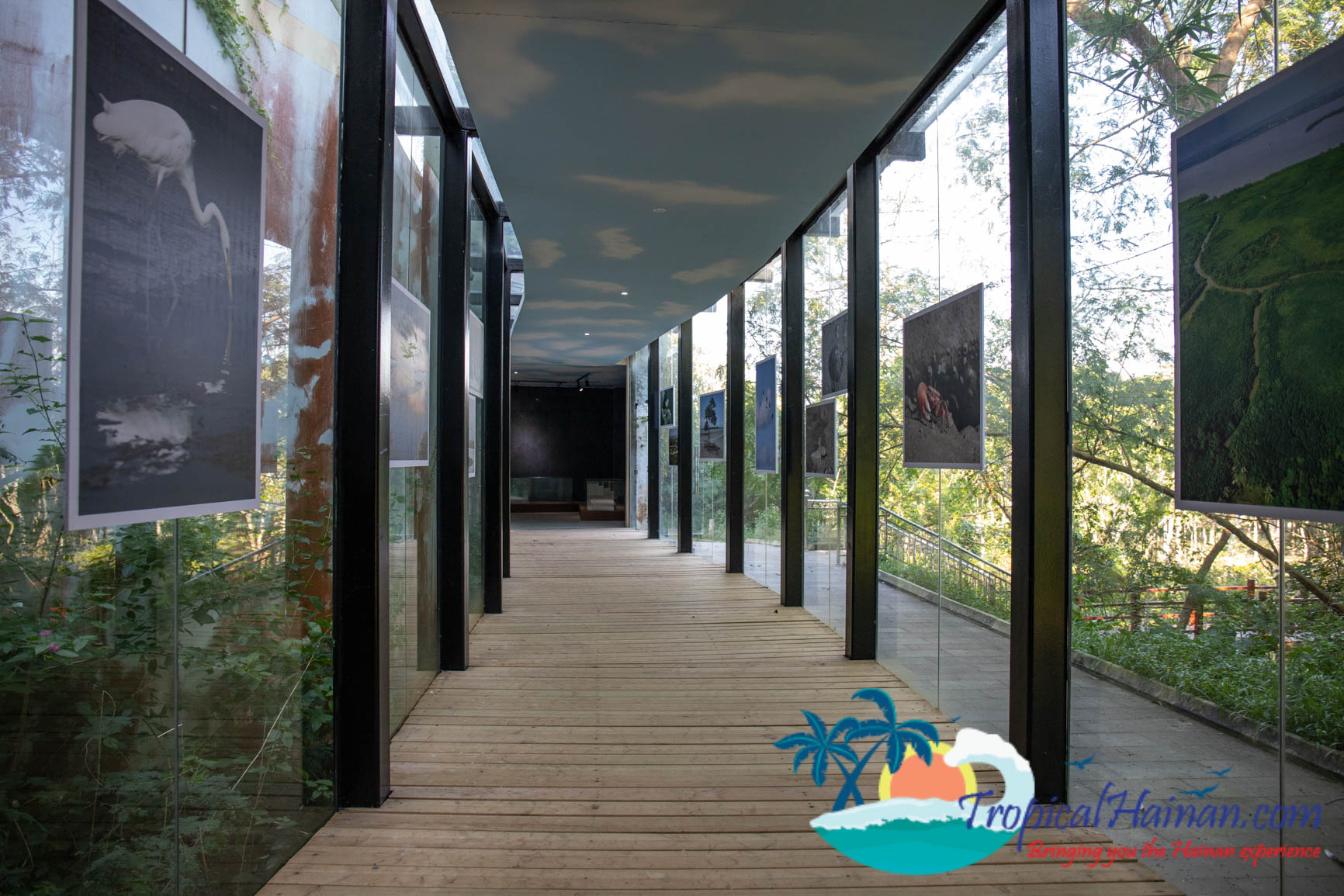
Just next to the carpark is a museum which has lots of information about the mangroves in English, there are two floors and to the rear of the museum a pathway which takes you into the mangrove marshes.
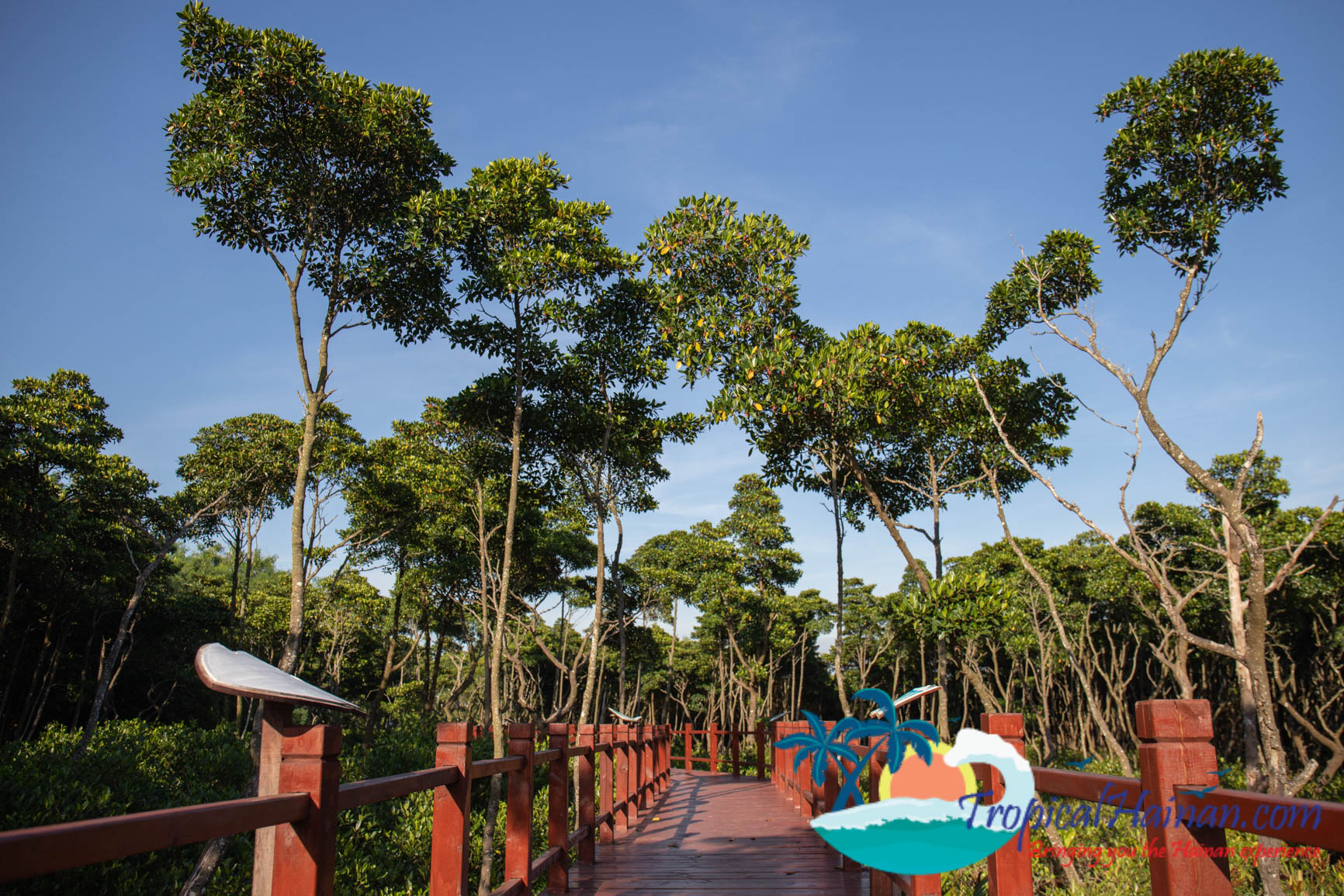



It is possible to take a short boat tour around the mangrove, tickets cost 60 yuan and the total length of the tour is around 30 minutes.
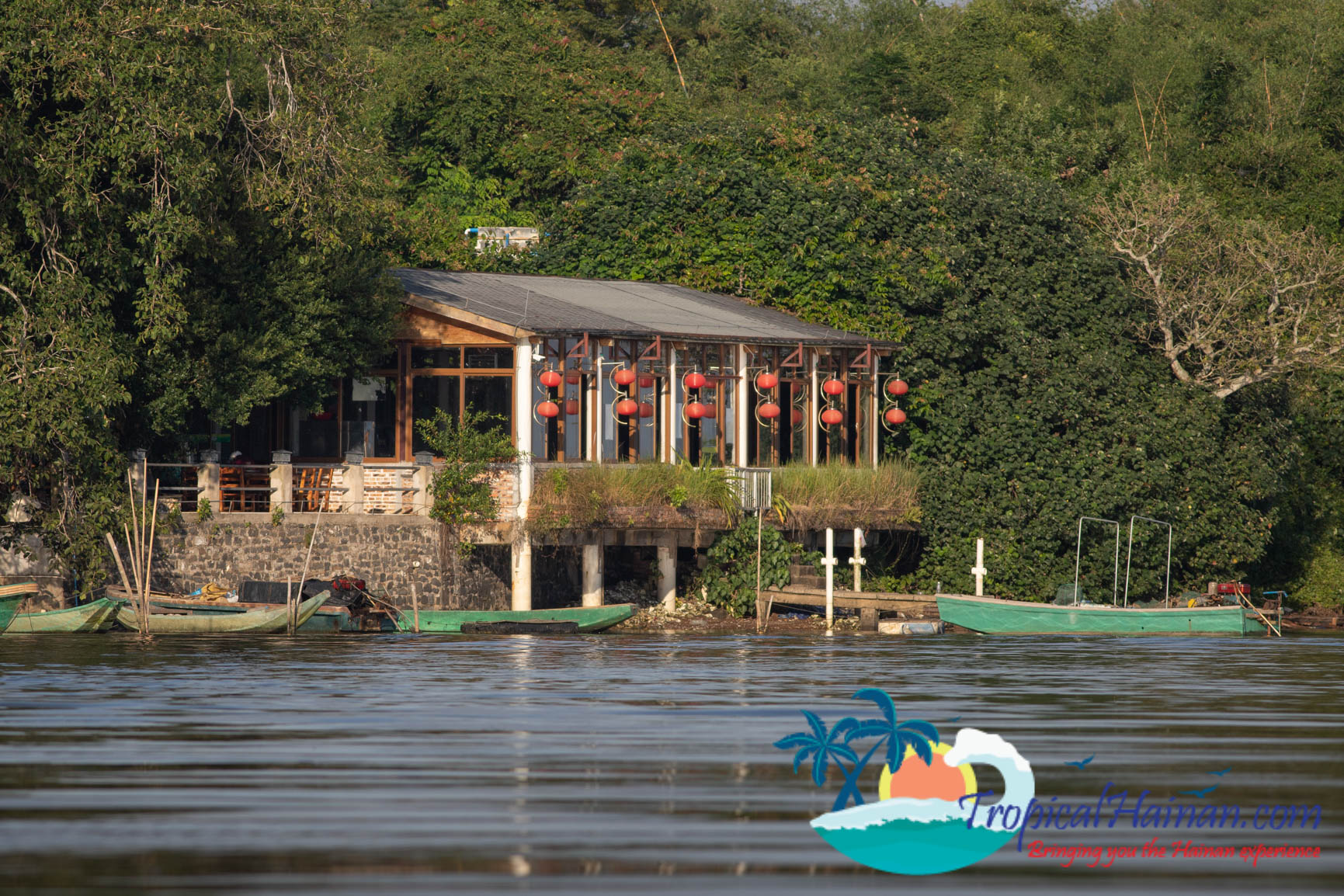
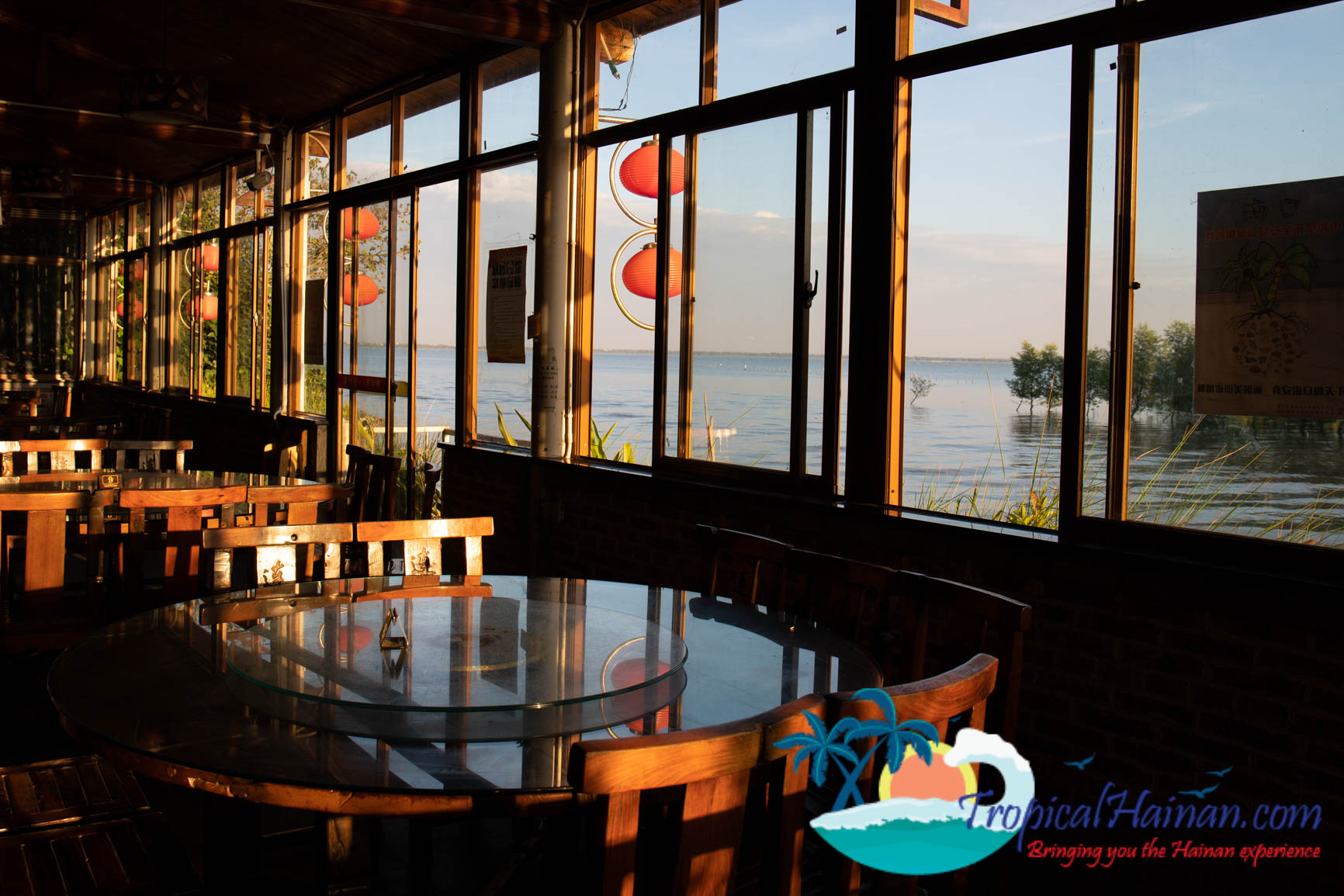
There are small restaurants next to the mangroves park. If you fancy a walk, around 2km up the road, there is an excellent seafood restaurant with tables that look out onto the mangroves. Restaurant pictured below.


Location
Address:东寨港红树林