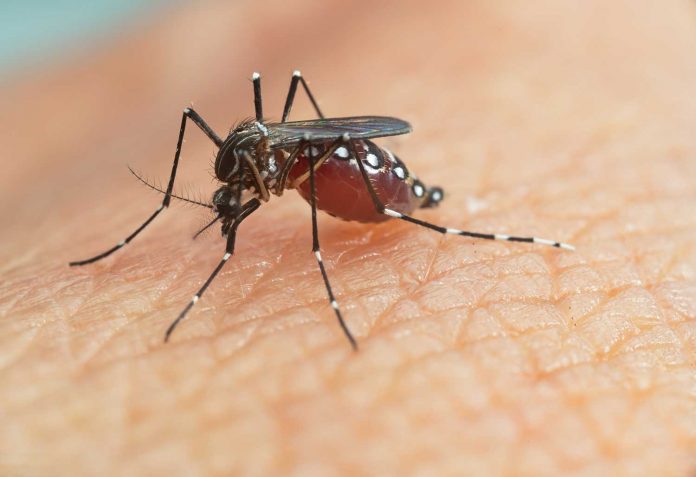
According to the Guangdong Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention, a total of 775 new cases of dengue fever were reported in the province during the week of September 9-15, an increase of 73 cases from the previous week.
Authorities have attributed the outbreak to high temperatures and wet weather, and increasing travel to dengue-prevalent places.
The outbreak is also thought to have been exacerbated by the week-long holiday celebrating China’s National Day.
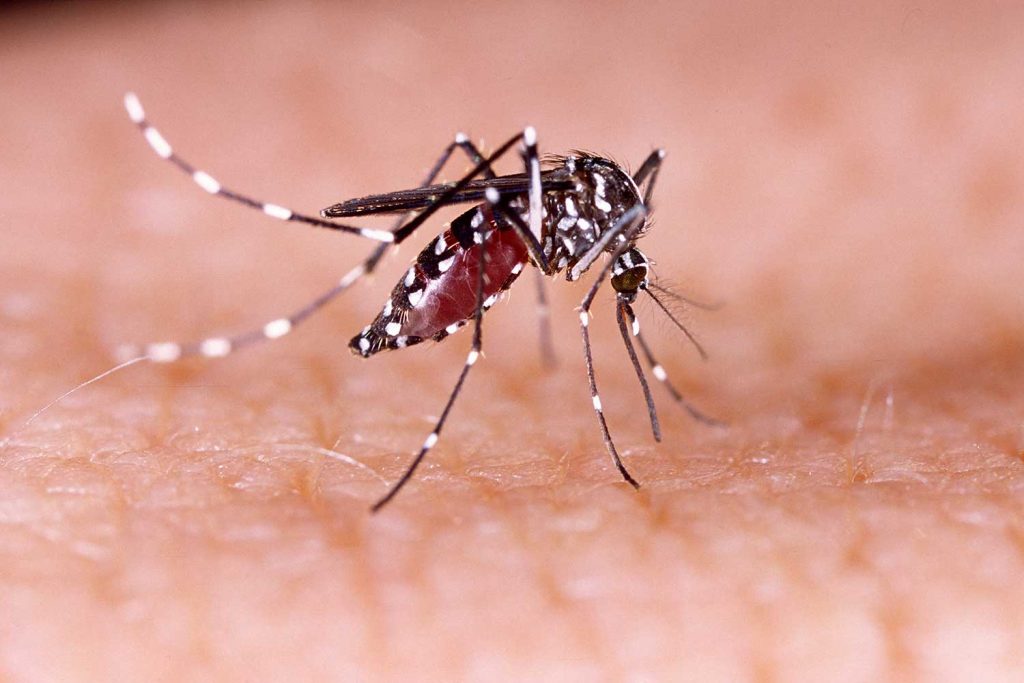
Dengue fever, caused by the dengue virus, is a mosquito-borne illness that can cause severe pain, leading it to be nicknamed “breakbone fever.” While Hainan Island had been free of dengue outbreaks for 28 years, it experienced a resurgence in September 2019. As the peak season for dengue fever typically spans from May to November, with the highest risk between August and October, it’s crucial to stay informed about the symptoms and take preventative measures.
Who is Most at Risk?
Dengue fever affects people of all ages, but certain groups are more vulnerable to severe cases. These include the elderly, infants, pregnant women, and individuals with chronic conditions. Moreover, those who have previously been infected with dengue are at higher risk of complications if exposed to a different strain of the virus.
How is Dengue Fever Transmitted?
Unlike illnesses that spread from person to person, dengue is transmitted through the bites of infected mosquitoes, specifically the Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti species, often referred to as “tiger mosquitoes.” The virus spreads in a cycle: a mosquito bites an infected person, the virus multiplies within the mosquito, and when the mosquito bites a healthy individual, the virus is transmitted.
Key Symptoms to Watch Out For

Dengue fever is often mistaken for the flu due to its early symptoms, but it has distinctive signs that require immediate attention:
- High Fever: A sudden rise in temperature, often reaching 39-40°C, within 24-36 hours.
- Pain: Severe headaches, joint pain, and muscle aches.
- Redness: Flushed face, neck, and chest.
- Rashes: A congestive or petechial rash on the limbs, trunk, or face.
In severe cases, dengue can lead to organ failure or even death. Because early symptoms are similar to the common cold, timely diagnosis and treatment are critical. If you experience these symptoms, seek medical attention without delay.
Effective Prevention Strategies
Given that there is no specific treatment or vaccine for dengue fever, prevention is the most effective approach. Here are some key ways to protect yourself and your family:
Mosquito Bite Prevention
- Wear Protective Clothing: Opt for light-colored, long-sleeved shirts and pants when outdoors, especially during peak mosquito activity from dusk to dawn.
- Use Mosquito Repellent: Apply repellents containing DEET or picaridin to exposed skin and clothing.
- Install Screens: Ensure your home is equipped with window and door screens to keep mosquitoes out.
- Sleep Under Nets: When in areas where dengue is prevalent, sleep under mosquito nets to reduce your risk of bites.
Eliminating Mosquito Breeding Sites
Mosquitoes breed in stagnant water, so it’s crucial to address potential breeding grounds around your home:
- Cover Water Containers: Keep water jars, tanks, and other containers sealed.
- Drain Standing Water: Regularly remove water from areas such as flower pots, tree holes, tires, construction sites, and rooftop drains.
- Clear Gutters and Drains: Ensure that drainage systems are free from blockages, mud, and weeds.
- Dispose of Unused Containers: Get rid of or invert empty cans, bottles, and other items that can collect water.
What to Do If You Suspect Dengue Fever
If you suspect you or a family member has dengue fever, it’s important to act quickly:
- Seek Medical Attention: Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the disease from progressing into a more severe form.
- Stay Hydrated: Dengue can cause dehydration due to fever and sweating. Drink plenty of fluids, such as water and rehydration solutions.
- Rest and Monitor Symptoms: Rest is essential for recovery. Watch for worsening symptoms such as vomiting, abdominal pain, or difficulty breathing, and seek urgent medical care if these occur.
- Avoid Certain Medications: Do not use non-prescription painkillers like aspirin or ibuprofen, as they can increase the risk of bleeding. Use paracetamol for pain relief, but only under medical supervision.
With dengue fever on the rise during peak season, prevention is key. By taking steps to avoid mosquito bites and eliminating potential breeding grounds, you can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
Stay vigilant, especially if you live in or travel to areas where dengue fever is prevalent, and seek medical care if symptoms arise. Early detection and appropriate treatment are essential for managing the illness and preventing complications.
Related article: Haikou People’s Hospital International Clinic Medical Service Guide