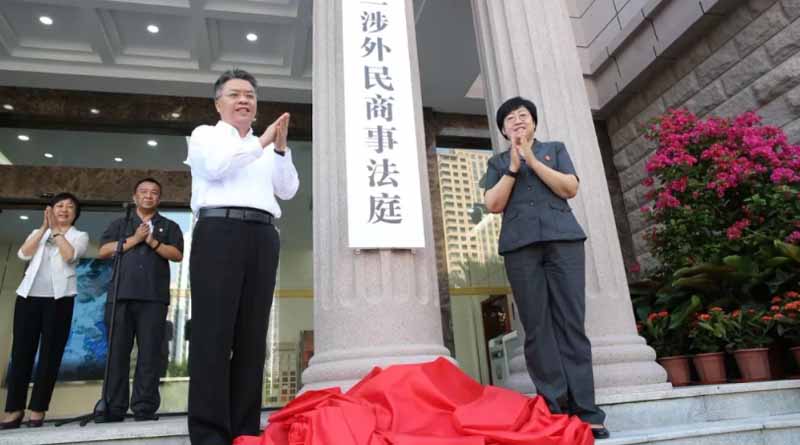
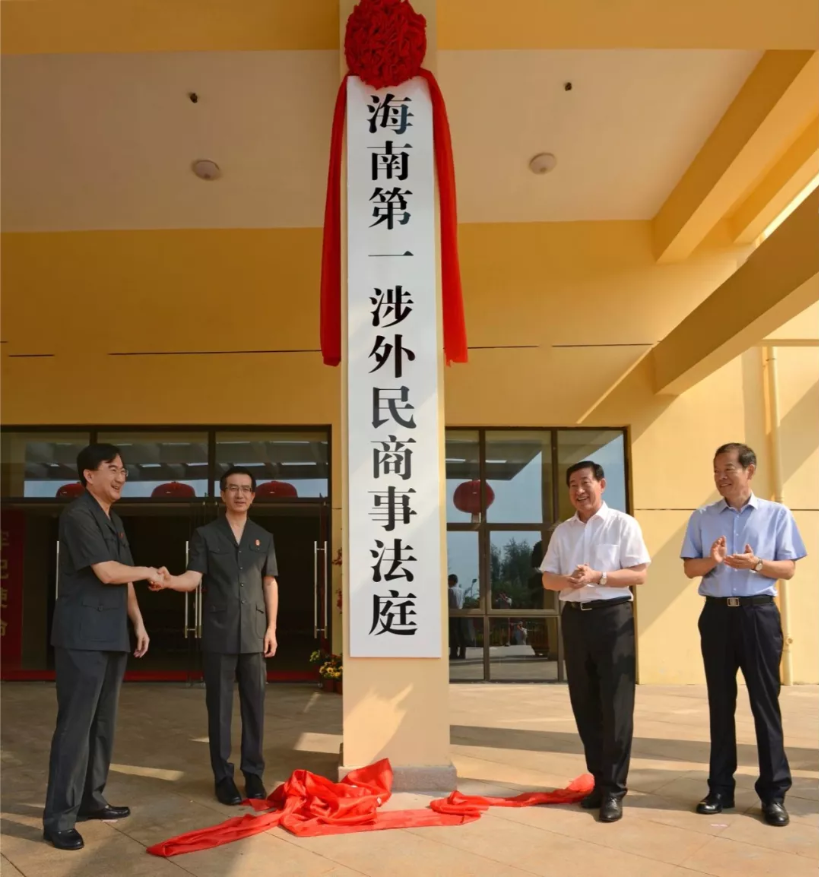
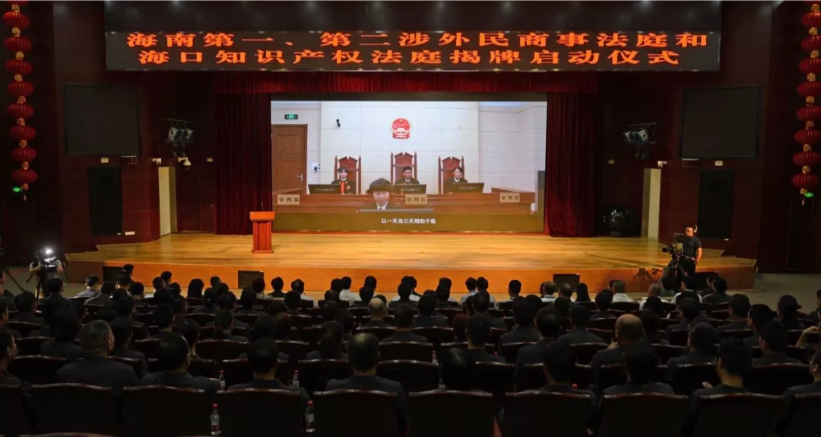
September 26, the opening ceremony of the Hainan first and second foreign civil and commercial courts and Haikou intellectual property court was held in Haikou and Sanya respectively.


In an address Lou Dongchuan stated, “The establishment of Hainan’s first and second foreign-related civil and commercial courts and the Haikou Intellectual Property court demonstrates the high importance the Party Central Committee attaches to Hainan. It is hoped that Hainan’s courts at all levels will understand the significance of Hainan’s comprehensive deepening of reform and opening up, seize opportunities, make bold innovations, and actively explore and make new contributions to the development of the people’s court’s, foreign-related civil and commercial trials and intellectual property trials.
Liu Xingtai commented that “The establishment of the three specialized courts is an important act of exploration and practice for Hainan Court’s active service and reform. It is a major measure for Hainan’s political and legal system to ensure the construction of the Hainan Free Trade Zone and the Free Trade Port with Chinese characteristics. Become a window to showcase Hainan’s image of the rule of law, and create a legal, international, and convenient business environment and a fair, unified, and efficient market environment for the construction of the Hainan Free Trade Zone and the free trade port with Chinese characteristics.”
“The construction of a free trade port provides an opportunity for a better and more powerful judicial services system and trial capabilities.”

It is understood that the Haikou Intellectual Property Court is the 20th special intellectual property court approved by the Supreme People’s Court and is located in the Haikou Intermediate Court.
The Hainan foreign related civil and Commercial Court is the first provincial-level and cross regional special court that has centralized jurisdiction over foreign-related civil and commercial cases.
The first foreign-related civil and Commercial Court is located in No.1 middle court of Hainan Province, with 11 cities and counties including Haikou City in the north of Hainan Province as well as Yangpu Economic Development Zone; the second foreign-related civil and Commercial Court is located in Sanya middle court, with 8 cities and counties including Sanya City in the south of the Province.
According to a spokesperson, “The establishment of two types of specialized courts is considered of great significance for the construction of the Hainan Free Trade Zone and the free trade port with Chinese characteristics.”
This English translation is for reference purposes ONLY and not a legally definitive translation of the original Chinese texts. In the event a difference arises regarding the meaning herein, the original Chinese version shall prevail.
Case jurisdiction
Centralised jurisdiction over the first instance of foreign-related civil and commercial cases with an amount of less than 5 billion Yuan within Haikou City, Sansha City, Danzhou City, Yangpu Economic Development Zone, Wenchang City, Qionghai City, Chengmai County, Tunchang County, Lingao County, Ding’an County, people’s Court of Qiongzhong Li and Miao Autonomous County, and Changjiang Li Autonomous County; the amount of the object of litigation within the above jurisdiction is to be less than 5 billion Yuan.
Types of cases accepted
Civil and commercial cases in which one or both of the parties are foreigners, stateless persons, foreign enterprises, or the habitual residence of one or both of the parties is outside the territory of the people’s Republic of China; civil and commercial cases in which the legal facts that generate, change or eliminate civil relations occur outside the territory of the people’s Republic of China, or the subject matter is outside the territory of the people’s Republic of China.
Civil and commercial cases involving Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan shall refer to the types involving foreign civil and commercial cases.
1 Materials to be submitted
Written indictment, copies shall be submitted according to the number of the opposite party, and the indictment should clearly state:
1. The name, gender, age, nationality, occupation, work unit and address of the parties, contact information, the name and address of the legal person or other organization, and the name, position and contact information of the legal representative or main person in charge;
2. Litigation request and the facts and reasons on which it is based;
3. Evidence and source of evidence; name, address and contact information of witnesses; the submitted materials shall be notarized by the notary office of the country where they are located and certified by the embassy and consulate of the people’s Republic of China in that country;
4. The standardisation of prosecution is one of the basic requirements of good faith litigation. In addition to the above content, it also includes mediation opinions, interpretation of applicable laws and other aspects. Please carefully read the “Notes” on “Standardization of Prosecution” carefully to avoid adverse consequences.
2 Required prosecution materials from the parties:
If the plaintiff is a domestic natural person or legal person, submit a copy of that person’s ID card, a copy of the business license of the legal representative, industrial and commercial registration information and unified social credit code;
If the plaintiff is an individual, enterprise or organization from a foreign country, stateless or from Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan, he / she shall submit the basic information and supporting materials for his / her subject qualification, and go through notarization and certification procedures or submit other supporting materials in accordance with the law.
If the plaintiff is a legal person or other organization in a foreign country, Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan, they shall also submit the resolution of the shareholders’ meeting, the resolution of the board of directors, the partnership agreement or the opinions of the person in charge that agrees to sue, and handle the corresponding notarization and certification procedures according to law.
For foreign, legal persons or other organizations to participate in the lawsuit, the identity documents submitted shall be notarized by the notary body of the country where they are located and authenticated by the embassy or consulate of the people’s Republic of China in that country, or the certification procedures stipulated in the relevant treaties concluded between the people’s Republic of China and the country where they are located shall be fulfilled.
3 The entrusted litigation agent must submit the following formalities for authorization:
1. Power of attorney;
2. If the client is a legal person, the identity certificate of the legal representative or person in charge shall be submitted;
3. A copy of the identity certificate of the agent (the lawyer’s agent must submit a letter from the law firm and a copy of the lawyer’s practice certificate);
4. Foreign parties in foreign-related civil and commercial litigations may entrust their own nationals as litigation agents or their lawyers as non-lawyer agents; officials of foreign embassies and consulates in China may be entrusted by their citizens to act in their personal names acting as a litigation agent, but not enjoying diplomatic or consular privileges and immunities in litigation;
Where a foreigner, stateless person, foreign enterprise or organization has no domicile in the territory of the people’s Republic of China entrusts a lawyer or other person of the people’s Republic of China to represent a lawsuit, the power of attorney sent or entrusted from outside the territory of the people’s Republic of China shall be certificated by a national notary office and certified by the embassy or consulate of the People’s Republic of China in that country, or fulfill the certification procedures stipulated in the relevant treaty concluded between the People’s Republic of China and that country;
5. The power of attorney signed by the legal representative of a foreigner, stateless person, foreign legal person, or other organization’s in front of the people’s court staff on behalf of the enterprise or organization, does not need to go through notarization, certification, or other formalities, but when signing the power of attorney, the identity certificate and entry certificate shall be presented.
The legal representative or person in charge of the foreign legal person or organization must also submit the notarization certification or other certification procedures issued by the legal person or organization, which proves that it has the right to sign an authorized power of attorney. The documentary proof of the certificate shall be indicated on the power of attorney by the staff of the people’s court;
The power of attorney signed by a foreigner or stateless person in China shall be notarized by a notary office in China, and it shall prove that the power of attorney is signed in China. The legal representative need not go through notarization, or other certification procedures;
6. Civil and commercial litigation agents involving Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan shall be conducted with reference to the foreign and commercial litigation agent regulations. Residents of Hong Kong and Macau who have obtained the qualifications of lawyer from Mainland China cannot act as lawyers in Mainland of China Litigation on civil and commercial cases outside the scope of the Announcement on Civil Cases (Ministry of Justice 136).
Note: the above copies must be submitted in the original for verification. In order to conduct the litigation more efficiently, if materials submitted by the parties to the people’s court are in a foreign language, the Chinese translation confirmed by a translation agency shall be submitted at the same time.
Cases where registration is not allowed
Although the registration system is now implemented in China, in order to maintain the normal order of litigation, the people’s court can still refuse to accept relevant cases in the following circumstances:
(1) bringing a suit in violation of the law or failing to comply with the provisions of the law;
(2) involving damage to the sovereignty and territorial integrity of a state;
(3) endangering State security;
(4) undermining the country and national unity;
(5) sabotaging state religious policies;
(6) the matter in question is not under the jurisdiction of the people’s court.
If there are slanders and personal attacks in the indictment, the parties shall amend them before bringing a lawsuit.
Circumstances in which a case can be filed for hearing
If you have any objection to the people’s court’s refusal to file a case, you can apply for a hearing according to legal procedures to safeguard your legitimate rights and interests.
(1) it is inadmissible according to law;
(2) the plaintiff disagrees with the notice regarding the completion and correction of the prosecution materials and insists on making up or correcting them;
(3) the Plaintiff still fails to meet the requirements for accepting the case after completing or correcting the prosecution materials;
(4) other circumstances in which the opinions of the prosecutor need to be heard in person.
In the hearing procedure the prosecutor has the right to apply for withdrawal, to make statements, to defend and to provide evidence on whether the prosecution meets the conditions for acceptance.
Application for evidence preservation and application for court investigation and evidence collection
In the event that evidence may be lost or difficult to obtain in the future, the parties may apply to the court for preservation of the evidence in the process of litigation. In case the evidence is likely to be lost or difficult to obtain in the future due to urgent circumstances, the interested parties may apply to the people’s court where the evidence is located, where the respondent has his domicile or where the case has jurisdiction for preservation of evidence before bringing a lawsuit or applying for arbitration.
If evidence preservation may cause losses to others, the people’s court shall order the applicant to provide corresponding guarantees.
The parties and their litigants who are unable to collect evidence on their own for objective reasons may apply to the court for investigation and collection. The application should be in writing and submitted to the court before expiration of the time limit for adducing evidence.
Circumstances in which property preservation can be applied for before litigation
If an interested party’s legitimate rights and interests will be harmed if it fails to apply for preservation immediately due to an emergency, it may apply to the people’s court in the place where the property is to be preserved, the place where the respondent has his domicile or has jurisdiction over the case for preservation measures before filing a lawsuit or applying for arbitration.
The applicant shall provide guaranty, and if it fails to provide guaranty, it shall rule to reject the application. After accepting the application, the people’s court must make a ruling within 48 hours; if it makes a ruling to take measures of preservation, the execution shall be started immediately.
If the applicant fails to file a lawsuit or apply for arbitration according to law within 30 days after the people’s court takes the preservation measures, the people’s court shall terminate the preservation.
Other ways to resolve disputes
In order to facilitate an economic and efficient settlement of disputes and reduce litigation risks and costs, Hainan first foreign civil and Commercial Court also has a case management office, which adheres to the principles of voluntary legality, simplicity, flexibility, efficiency and cost effectiveness, and can help you solve disputes.
(1) the parties may choose mediators from a list of specially invited mediation organizations and mediators provided by the case management office, or they may choose mediators or mediation institutions outside the list for mediation.
(2) before the registration and filing of a case, the case management office may appoint a specially invited, suitable mediation organization or mediator or court personnel to mediate the case.
(3) after the case is registered, the personnel of the court shall mediate. If a mediation agreement is reached, the presiding judge shall issue a civil mediation statement after examination according to law, and the parties may apply for exemption from the litigation expenses.
(4) In the case of mediation before filing, the mediation period generally does not exceed 30 days. If mediation is indeed possible, the mediation period shall not exceed 60 days. If the parties agree to extend the mediation period, they are not subject to this limit.
The time limit for mediation after filing a case is 20 days. If both parties agree to extend the mediation period, this restriction shall not apply, and the extended mediation period shall not be included in the trial period.
(5) if a party applies for withdrawal of a lawsuit due to self-reconciliation before a court session, the case acceptance fee shall be exempted.
(6) parties may face adverse consequences if they do participate in mediation without justifiable reasons after choosing the mediation procedure.
How to appeal
If a party refuses to accept a judgment or ruling of first instance and has a domicile within the territory of the People’s Republic of China, he shall have the right to submit an appeal within 15 days from the date of service of the judgment or ruling and appeal to the higher people’s Court of Hainan Province.
If a party refuses to accept a judgment or ruling of first instance and has no domicile within the territory of the People’s Republic of China, he shall have the right to submit an appeal within 30 days from the date of service of the judgment or ruling and appeal to the higher people’s Court of Hainan Province.
Case acceptance fee
After the case is successfully filed, the parties need to pay the case acceptance fee within 7 days, otherwise, it will be handled as a withdrawal.
The specific payment method and case acceptance fee shall be in accordance with the provisions of the measures for the payment of litigation fees of the Supreme People’s court.
Other considerations
(1) pay attention to the submission of defense opinions within the time limit. If the defendant has no domicile within the territory of the People’s Republic of China, he shall within 30 days from the date of receiving the copy of the statement of complaint, make a written reply to state his opinions on the plaintiff’s claim, facts and reasons.
(2) the court may provide translation assistance. The language and writing commonly used in the People’s Republic of China shall be applied in the trial of foreign-related civil and commercial cases. If the parties require translation, they can do so, and the cost shall be borne by the parties.
(3) Note that the following actions in a lawsuit may bear legal liability: false lawsuits, malicious lawsuits, and unreasonable lawsuits including disciplinary action, fines and detention; if the case constitutes a crime, criminal liability shall be investigated according to law.
Related article: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) about services for foreigners’ work permit in China part 1